
Also, for a particular disease there may be several diagnostic tests invented, where each of the tests is subject of one or more studies. One may want to combine such studies to get a good picture of performance of the test, a meta-analysis.
Usually there are several studies where performance of the diagnostic test is measured by some statistic. The flexibility of POR model, coupled with ease with which it can be estimated in familiar software, suits the daily practice of meta-analysis and improves clinical decision-making.Ī diagnostic test, in its simple form, tries to detect presence of a particular condition (disease) in a sample.
#Comprehensive meta analysis odds ratio code#
Also we provide code to convert numerical results into graphical ones, like forest plots, heterogeneous ROC curves, and post test probability difference graphs. Furthermore, we provide code for converting ORs into other measures of test performance like predictive values, post-test probabilities, and likelihood ratios, under mild conditions.
#Comprehensive meta analysis odds ratio how to#
In the paper we demonstrate how to formulate the model for a few real examples, and how to use widely available or popular statistical software (like SAS, R or S-Plus, and Stata) to fit the models, and estimate the discrimination accuracy of tests. One may expand the domain of the POR model to cover dependent studies, multiple outcomes, multiple thresholds, multi-category or continuous tests, and individual-level data. The POR model does not assume homogeneity of ORs, but merely specifies a relationship between the ORs of the two tests. We propose a model, the proportional odds ratio (POR) model, which makes no assumptions about the shape of OR p, a baseline function capturing the way OR changes across papers.

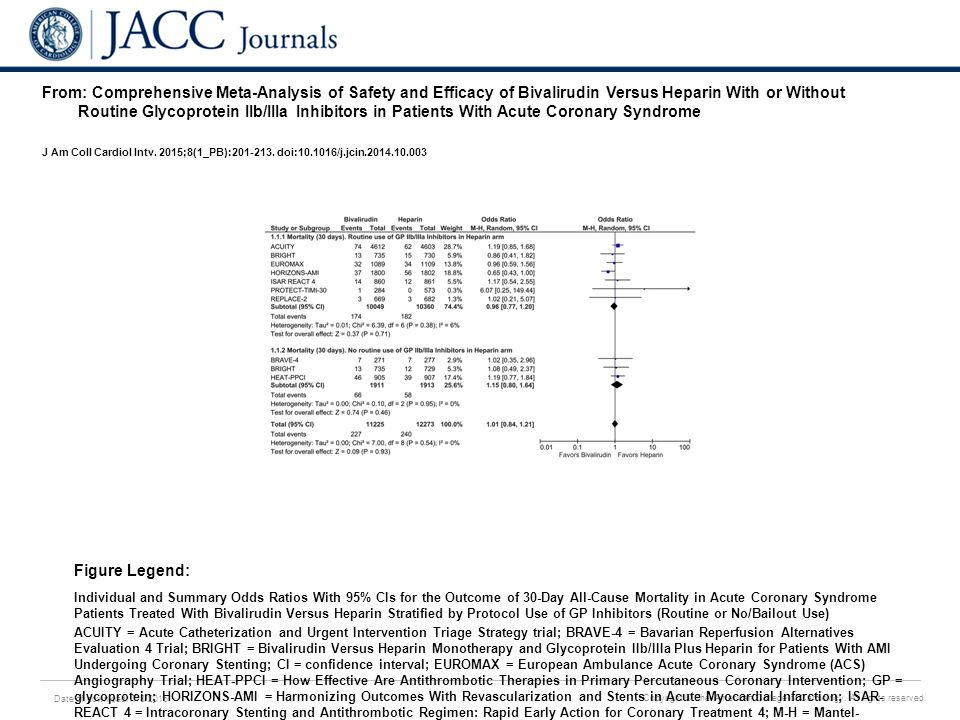
Also the collection of tests studied may change from one paper to the other, hence incomplete matched groups. Some of the papers may have studied more than one test, hence the results are not independent. Assume there are two or more tests available for the disease, where each test has been studied in one or more papers. Because their results are unreliable, use of the conventional methods for meta-analysis of ORs should be discontinued.Consider a meta-analysis where a 'head-to-head' comparison of diagnostic tests for a disease of interest is intended. The modest additional programming required should not be an obstacle to adoption of the alternative methods. Programming is straightforward in the 3 software packages an appendix, Suppemental Digital Content 1 () gives the details. In the example, point estimates and confidence intervals for the overall log-odds-ratio differ between the conventional and alternative methods, in ways that can affect inferences. We demonstrate the use of SAS, Stata, and R software for the analysis. We summarize the fixed-effect and random-effects approaches to meta-analysis describe conventional, approximate methods and alternative methods apply the methods in a meta-analysis of 19 randomized trials of endoscopic sclerotherapy in patients with cirrhosis and esophagogastric varices and compare the results. We aim to raise awareness of methods that avoid the conventional approximations, can be applied with widely available software, and produce more-reliable results. A well-developed alternative approach avoids the approximations by working directly with the numbers of subjects and events in the arms of the individual trials. Although the problems have been documented in the literature for many years, the conventional methods persist in software and applications. That approach, however, has several shortcomings, arising from assumptions and approximations, that render the results unreliable. The customary methods of estimating an overall OR involve weighted averages of the individual trials' estimates of the logarithm of the OR. Many systematic reviews of randomized clinical trials lead to meta-analyses of odds ratios (ORs).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
